Xestoleberis vietnamensis, Dung & Tsukagoshi, 2018
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/ 10.11646/zootaxa.4472.1.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:68A4616A-EC22-4A2D-A575-DCBD03BE119D |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5990671 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/0382DE2A-FFF2-FFFD-50CE-4B8FFE24FAC9 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Xestoleberis vietnamensis |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Xestoleberis vietnamensis View in CoL sp. nov.
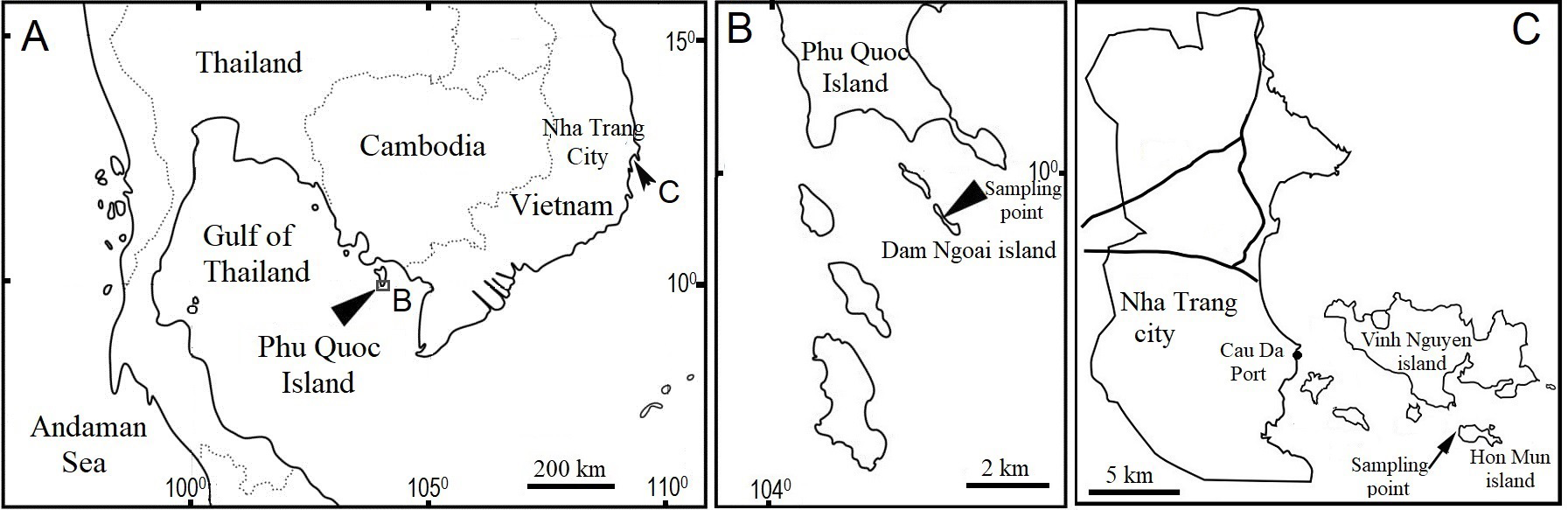
Type series. All specimens were collected at the coral reef in Dam Ngoai Island , Phu Quoc Marine Protected Area, Phu Quoc Island, southwest of Vietnam, 9°59'42"N, 104°02'17"E ( Fig. 1A,B View FIGURE 1 ) in November 2014. The substrate consisted mainly of very coarse sand, dead coral and algae. Holotype: SUM-CO-2429 (Soft parts and a right valve of adult male; soft parts were mounted on a glass slide using “Neo Shigaral” as mounting agent, and the carapace was mounted on a cardboard slide with single hole). Paratypes: 5 males (SUM-CO-2431, 2433, 2434, 2435, 2436) GoogleMaps , 2 females (SUM-CO-2430, 2432); soft parts mounted on a glass slide and carapaces on a cardboard slide with single hole; other specimens (carapaces) are kept on a cardboard slide with single hole.
Etymology. “From Vietnam ”: holotype specimen was collected from Dam Ngoai Island, Phu Quoc Marine Protected Area in Phu Quoc Island, Southwest of Vietnam.
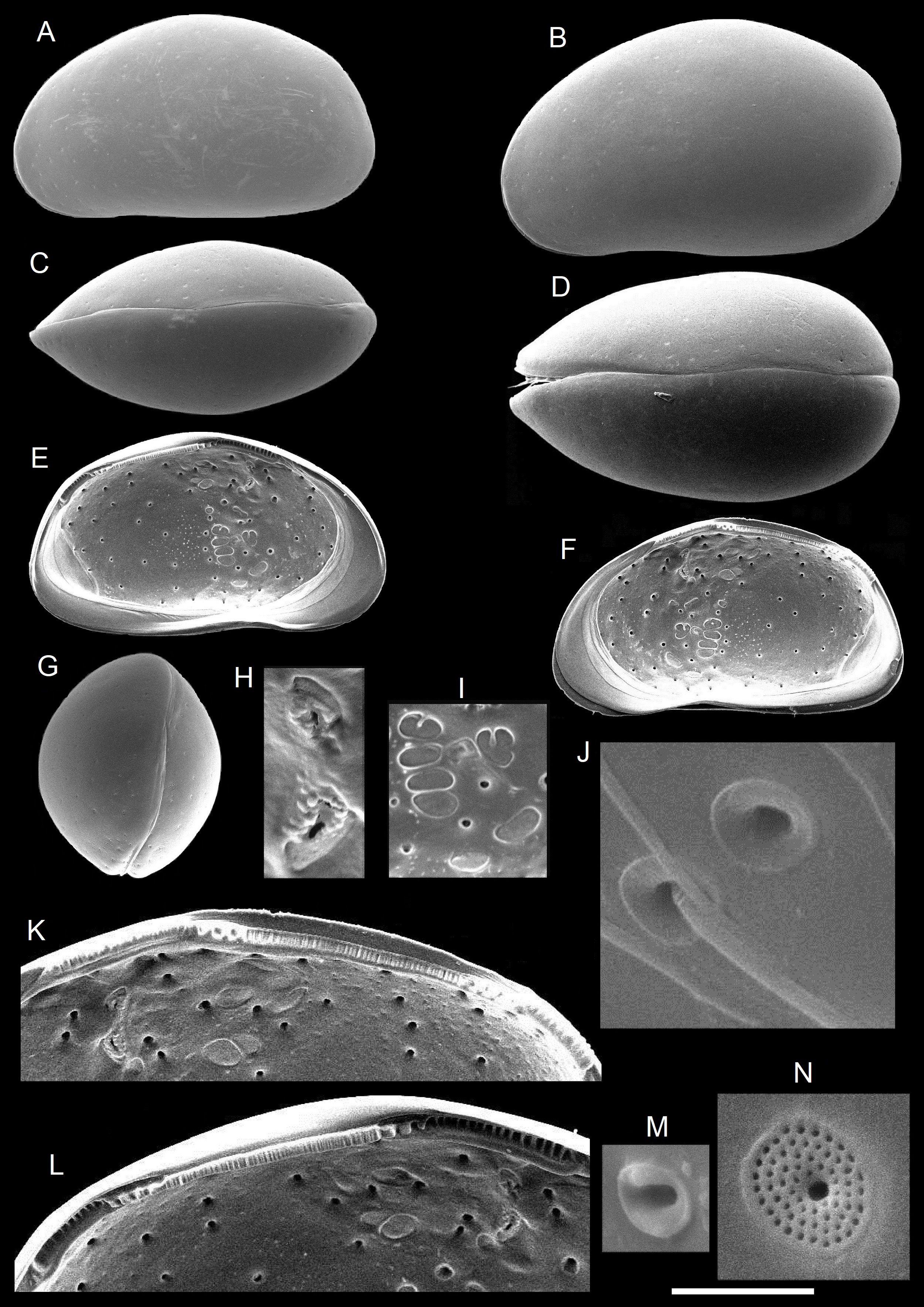
Diagnosis. Carapace inflated, subreniform to subovate in lateral view, showing sexual dimorphism in shape; dorsal margin rounded downward, ventral margin weakly sinuous as oral concavity. Posterior margin rounded in female, more angular in male. Living specimens white. Frontal muscle scar trefoil-Y-shaped. Four adductor muscle scars isolated, arranged in sub-vertical row, upper one U-shaped ( Fig. 6I View FIGURE 6 ). “ Xestoleberis- spot” divided into two parts ( Fig. 6H View FIGURE 6 ). Carapace consisting of two types of normal pores, lip-type ( Fig. 6M View FIGURE 6 ) and sieve-type ( Fig. 6N View FIGURE 6 ). Fourteen lip-type pores, while others are sieve-type pores. Male copulatory organ with subquadrate capsule, large distal lobes, left one terminating with small spine and right one rounded.
Description. Carapace ( Fig. 6 View FIGURE 6 ). Adult carapace size sexually dimorphic, males smaller than females ( Fig. 6A, B View FIGURE 6 ). Carapace elongate-oval in dorsal view ( Fig. 6C, D View FIGURE 6 ), with bluntly pointed anterior end, and narrowly rounded posterior end; almost circular to oval in posterior view ( Fig. 6G View FIGURE 6 ). Hinge antimerodont ( Fig. 6K, L View FIGURE 6 ) with welldeveloped teeth and sockets in anterior and posterior hinge elements. Median element strongly curved and finely crenulated. Frontal muscle scar trefoil-Y-shaped. Four adductor muscle scars isolated, arranged in sub-vertical row, upper one U-shaped ( Fig. 6I View FIGURE 6 ). “ Xestoleberis- spot” strongly divided into two parts ( Fig. 6H View FIGURE 6 ). Carapace consisting of two types of normal pores, lip-type ( Fig. 6M View FIGURE 6 ) and sieve-type ( Fig. 6N View FIGURE 6 ). Marginal pores funnel-type pore ( Fig. 6J View FIGURE 6 ). Both sexes with 14 lip-type pores, while others are sieve-type pores.
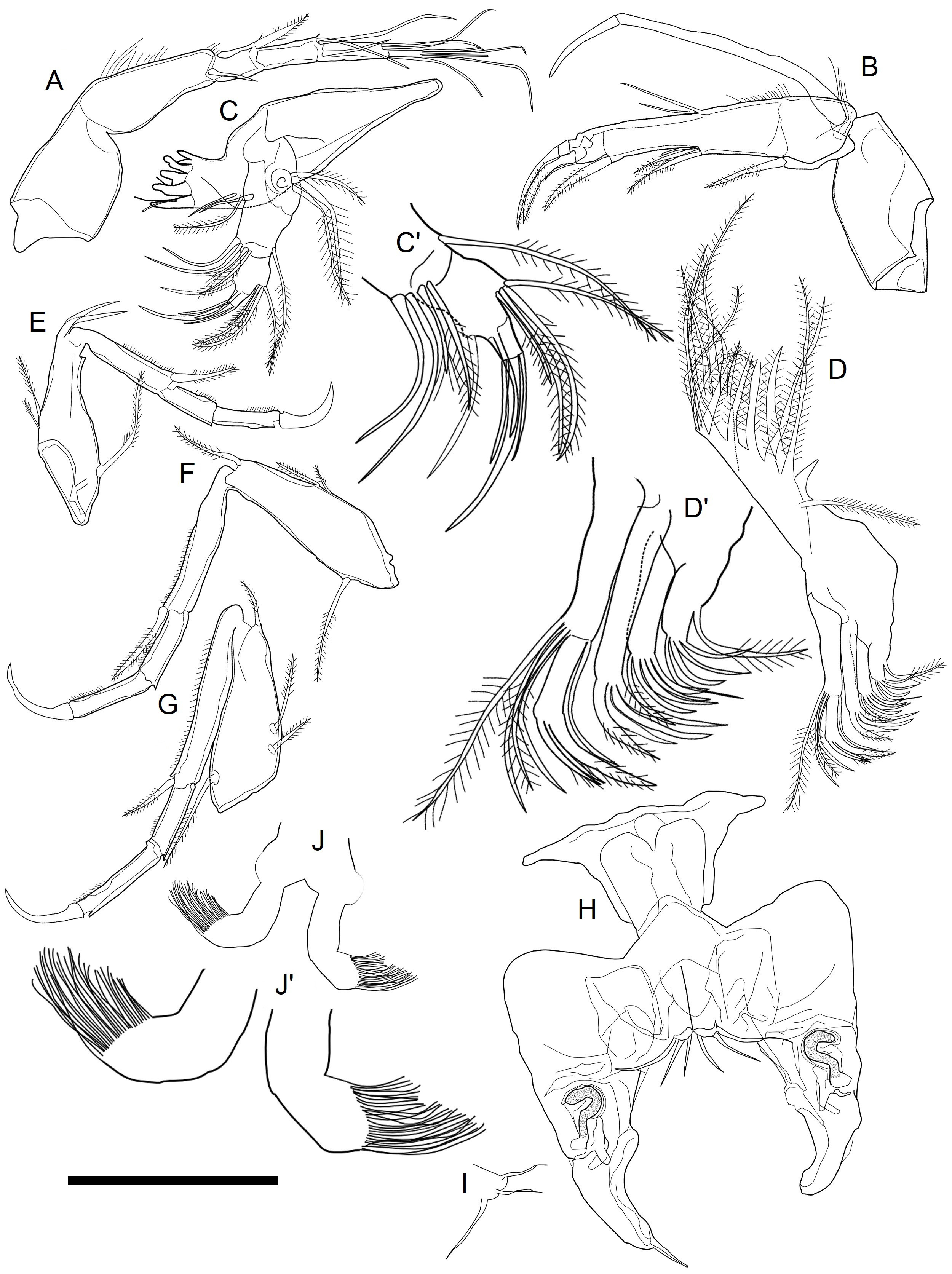
Antennula ( Fig. 7A View FIGURE 7 ). Six articulated podomeres, length ratios from proximal to distal 25:24:7:13:1:6, width of podomeres decreasing in this order. First podomere elongated pentagonal without seta. Second podomere elongate rectangular with setulae along anterior-distal margin, 1 short simple apical seta at posterior corner. Third podomere small, short, trapezoidal with 1 hirsute apical seta at anterior corner. Fourth podomere elongated rectangularly with 1 hirsute seta on posterior distal end, 1 medium-length and 1 short hirsute apical seta at anterior corner. Fifth podomere elongated rectangularly with 1 long seta on posterior distal end, 1 long and 1 medium-length apical seta at anterior corner. Sixth podomere very small, rectangular with 1 medium-length aesthetasc “Ya,” and 1 short seta and 2 long setae on distal end.
Antenna ( Fig. 7B View FIGURE 7 ). Consisting of four articulated podomeres, length ratios from proximal to distal 30:12:30:5, width decreasing in this order. First podomere with very long stout two-joined exopodite (=spinneret seta) at anterior distal end. Second podomere trapezoidal with relatively long setules along proximal anterior margin and 1 hirsute seta on posterior-distal end. Third podomere elongated bearing relatively long setulae on proximal anterior margin, 1 short aesthetasc “Y” and 2 hirsute setae protruding from posterior, 2 simple setae from anterior edges at proximately mid-length, and 1 hirsute robust seta at apical posterior corner. Fourth podomere very short and small with 1 reduced seta and 2 stout and chelate setae on distal end.
Mandibula ( Fig. 7C View FIGURE 7 , C’). Five articulated podomeres. Coxa stout, bearing 6 teeth on medial edge and 1 seta on anterior margin. Basis bearing exopodite with 3 plumose setae, 1 simple seta at posterior corner and 1 hirsute seta at ventro-distal end. First podomere of endopodite bearing 1 hirsute seta antero-distally, 2 very long and 2 shorter hirsute setae ventrally. Second podomere of exopodite consisting of 4 apical setae at anterior corner, 1 apical seta at posterior-distal corner and 1 seta on distal end. Third podomere of exopodite with 2 simple setae and 1 claw-like seta at distal end.
Maxillula ( Fig. 7D View FIGURE 7 , D’). Exopodite a thin branchial plate, with 16 long plumose setae and 1 hirsute reflexed seta. Basal podomere bearing endopodite and 3 endites. Endopodite consisting 2 podomeres and bearing 4 hirsute setae at anterior distal end of first podomere, and 3 hook-shaped hirsute setae (1 seta very large and 2 setae smaller) on distal end, 1 simple seta on ventral distal end of second podomere. Three endites bearing 4, 5 and 4 hirsute setae on distal end, respectively. Third endite also consisting of long seta on ventral proximal margin, stout proximally with medium-length setulae.
Fifth limb ( Fig. 7E View FIGURE 7 ). Four articulated podomeres bearing terminal claw-like seta, length ratios from proximal to distal 15:10:5:6. First podomere with 1 short and 1 medium hirsute seta in middle of anterior margin, 1 long hirsute seta at one-fourth from posterior proximal end and 2 hirsute setae at anterior apical corner. Second podomere with setulae along anterior distal margin and 1 hirsute seta at anterior apical corner. Third and fourth podomeres with setulae along anterior distal margin and without seta.
Sixth limb ( Fig. 7F View FIGURE 7 ). Consisting of four articulated podomeres, terminating with claw-like seta, length ratios from proximal to distal 17:12:7:7. First podomere carrying 1 short and 1 medium hirsute seta in middle of anterior margin, 1 very long hirsute seta at one-fourth from posterior proximal end and 1 hirsute seta at anterior apical corner. Second podomere with setulae along anterior distal margin and 1 hirsute seta at anterior apical corner. Third and fourth podomeres with setulae along anterior distal margin and not bearing seta.
Seventh limb ( Fig. 7G View FIGURE 7 ). With four articulated podomeres, terminating with claw-like seta, length ratios from proximal to distal 11:11:4:6. First podomere carrying 1 short hirsute anterior margin seta at one-fourth and 1 long hirsute seta on anterior margin of one-third from proximal end, 1 long hirsute seta at one-fifth from posterior proximal end and 1 hirsute seta at anterior apical corner. Second podomere with setulae along anterior margin and 1 hirsute seta at anterior apical corner. Third and fourth podomeres with setulae along anterior distal margin and not carrying seta.
Male copulatory organ ( Fig. 7H View FIGURE 7 ). Basal capsule subquadrate. Distal lobes large and thin, distally asymmetrical; left lobe terminating like spine, right lobe with rounded tip. Ejaculatory duct conspicuous and terminating on distal lobe.
Furca ( Fig. 7I View FIGURE 7 ). With one long seta and two short hirsute setae, located on posterior distal ward of male copulatory organ.
Brush-shaped organ ( Fig. 7J View FIGURE 7 , J’). Y-shaped in general; consisting of pair of branches with approximately 26 fine setae on each distal margin.
Dimensions. See Table 1.
Remarks. The carapace of Xestoleberis vietnamensis sp. nov. is highly similar to that of X. hanaii Ishizaki, 1968 ; X. sesokoensis Sato & Kamiya, 2007 ; and X. ryukyuensis Sato & Kamiya, 2007 . However, this species is smaller than X. hanaii and X. sesokoensis , but larger than X. ryukyuensis . The morphology of the male copulatory organ of this species is different from that of X. ryukyuensis , but similar to that of X. hanaii , X. porthedlandensis Hartmann-Schröder & Hartmann, 1978 , and X. sesokoensis . However, the copulatory duct of this species is question-mark shaped and thicker than that of X. hanaii and X. sesokoensis . The ratio of the length of the distal lobe to the length of the whole male copulatory organ of this species is smaller than that of X. hanaii . Furthermore, the distal lobes of the male copulatory organ of X. vietnamensis sp. nov species are more slender than those of both X. hanaii and X. porthedlandensis .
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |